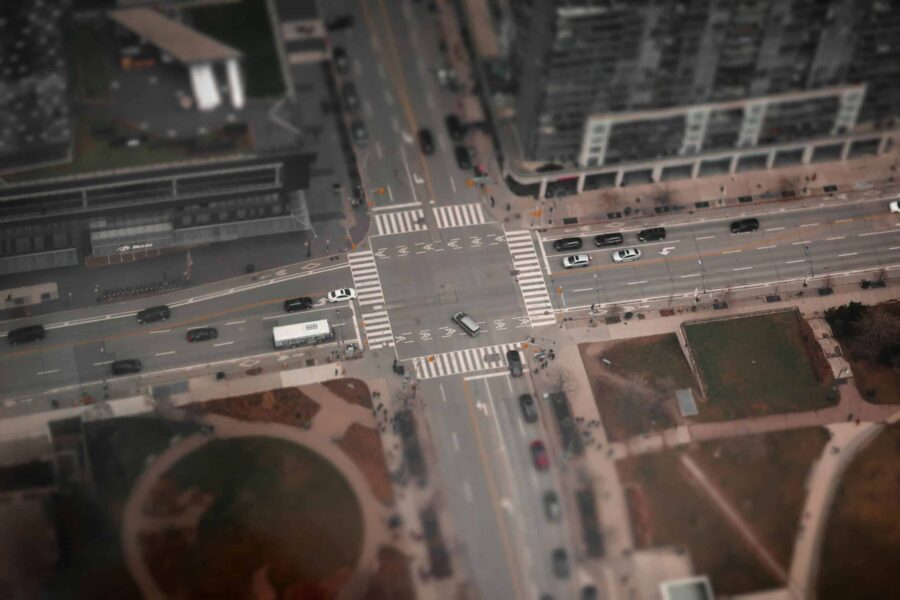
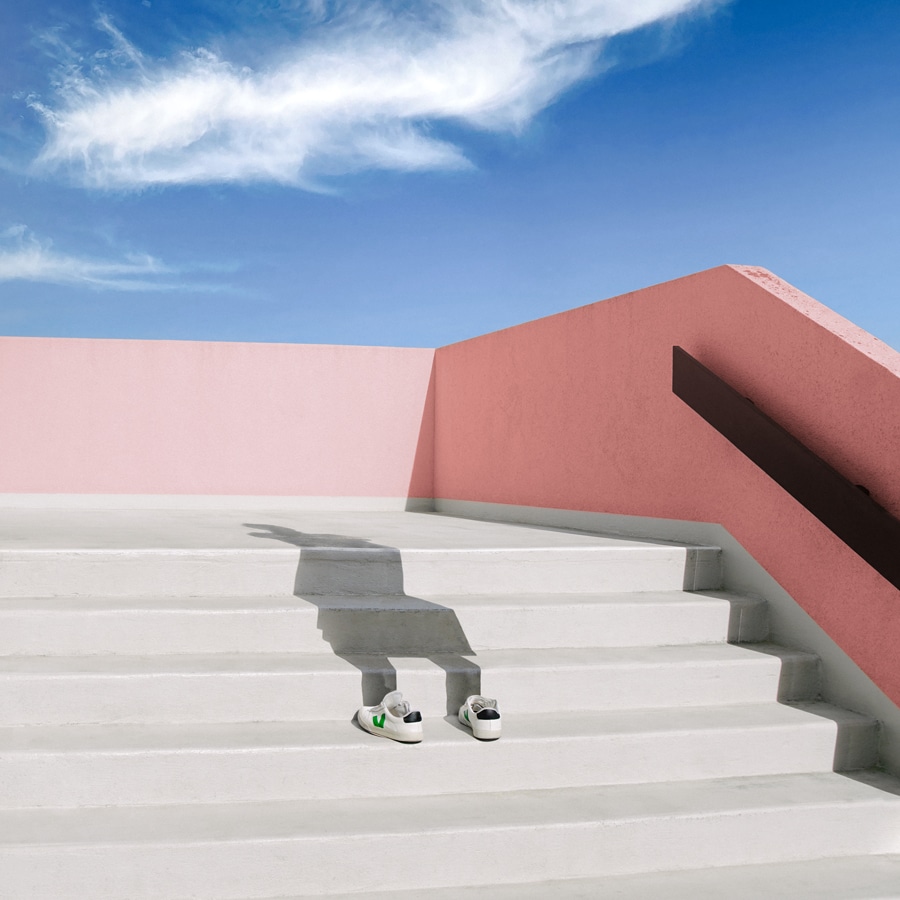
Tilt-shift is a photography technique mostly associated with miniature-like landscapes. It involves manipulating the camera’s lens to alter the plane of focus and depth of field. This, in turn, creates an illusion that can transform a vast scene into a seemingly tiny model.
Tilt-shift photography has been around for decades, and is enjoyed by photographers around the globe. This technique is going through another round of broader popularity–mastering it is well worth it if you want to advance your career and explore a new photography style you might end up loving. Learning all about tilt-shift photography isn’t just about getting a new technique in your arsenal. It’s also a way to expand your creative vision, explore a new perspective, and challenge your ideas about composition, focus, and storytelling.
Whether exploring tilt-shift photography for artistic expression, architectural and real estate photography, or another reason, this style will bring vast possibilities and invite you to see the world through a different lens.
In this article, we dive into the singular style of tilt-shift photography and provide you with the knowledge you need to elevate your photography skills in this arena.
Origins and Evolution of Tilt-Shift Photography
Tilt-shift photography produces fascinating images—and its origins are no less interesting.
The concept of tilt-shift photography originated in the early days of the medium refers to a technique used in large-format cameras. Early cameras had bellows, which photographers could manipulate to change the angle and position of their lens relative to the film plane.
As the technique evolved, specialized lenses were introduced in the mid-20th century. These specialized lenses made it possible for photographers to manipulate the lens plane without handling bulky and complex large-format cameras.
Over the years, tilt-shift lenses have been further refined to feature advanced designs and capabilities. There are now lenses that allow greater precision, easier handling, and wider applications, making them important tools for architectural and landscape photographers.
Thanks to the availability of improved equipment, the tilt-shift technique later amassed more interest from photographers in different genres. It’s used primarily in architectural and interior photography to correct perspective distortions in rooms and buildings and to create the miniature effect in landscape photography, but you can also find examples of tilt shift photography being used for artistic exploration, social media, viral trends, and more.
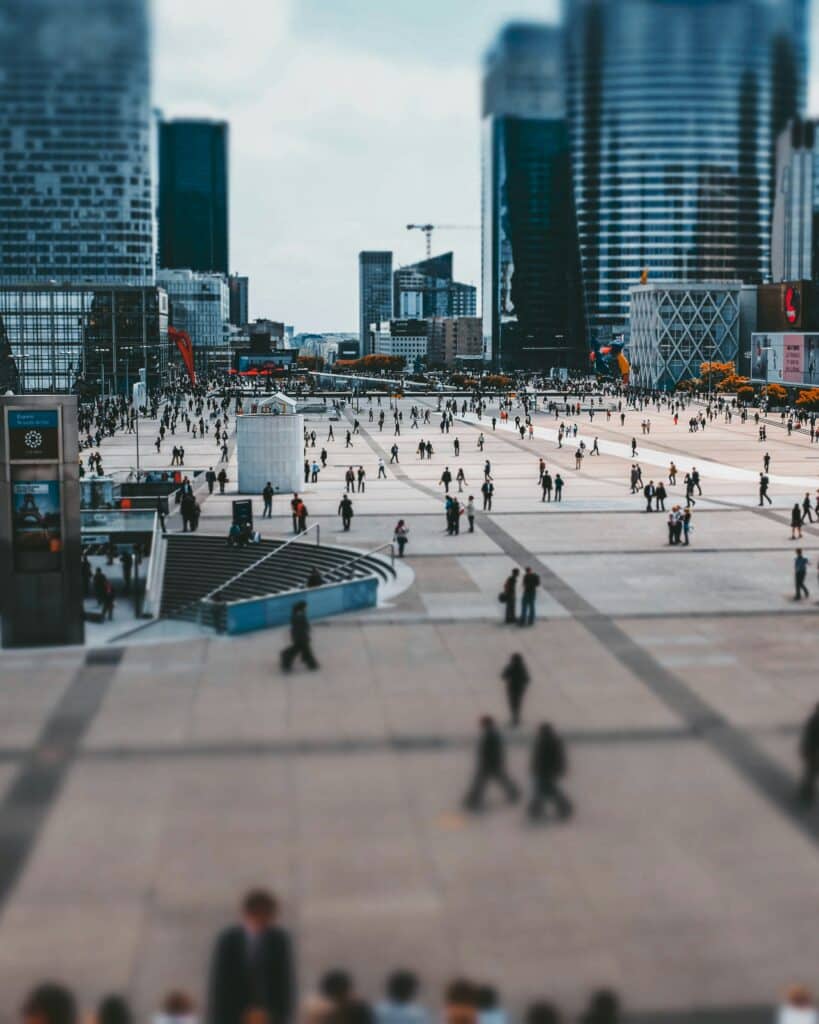

Understanding the Basics of Tilt-Shift Photography
Tilt-shift photography is based on the technique of manipulating focus and perspective. It allows photographers to capture and present images in an unexpected way. To understand tilt-shift photography, let’s first explore tilt, shift, and the equipment needed for this technique.
Tilt
Tilt refers to how a lens is angled narrative to the image sensor of the film plane in the camera. When the lens is tilted, the plane of focus changes. Normally, the plane is parallel to the sensor but tilting alters it and allows selective focus.
Tilt is often used to emphasize specific parts of a scene or create a miniature effect.
Shift
Shift is the act of moving the lens in different directions, whether up, down, or sideways, relative to the image sensor. It’s a technique used in architectural photography to control perspective.
Shift can allow the photographer to capture a tall building while keeping the camera level. This helps prevent the convergence of vertical lines.
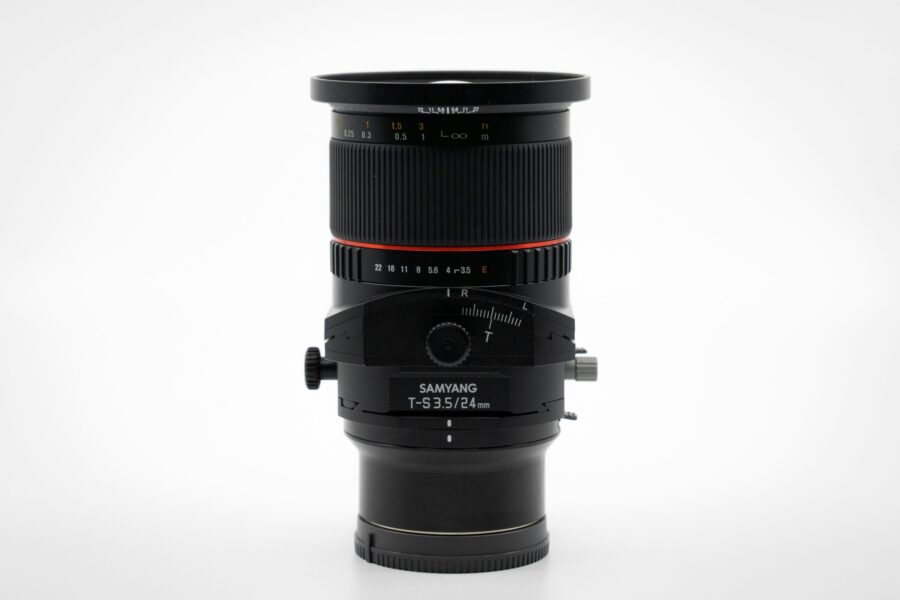
Equipment Required for Tilt-Shift Photography
Tilt-shift photography requires specialized lenses that are designed primarily for the technique. These lenses allow the photographer to control the tilt and shift movements precisely. Some photographers still do this the old-school way, using large-format cameras with moveable bellows to achieve the desired effect.
While tilt-shift lenses are the primary tool to achieve tilt-shift photography, post-processing software can also achieve the effect. Although post-edits can mimic the effect, it’s less precise and lack the organic quality of lens-based tilting and shifting.

Top 10 Techniques to Master Tilt-Shift Photography
Mastering tilt-shift photography is an excellent way to enhance your skill set and explore new means of creative expression. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned photographer looking to explore the tilt-shift photography style, here are the top 10 techniques you should focus on mastering.
1. Correct Camera Positioning
First is how to position your camera. You should maintain a leveled position to better control the perspective and avoid unintended distortions. A sturdy tripod can help with this, assisting you in ensuring stability. A tripod can be a valuable tool for tilt-shift photography, allowing you to make precise adjustments without losing stability.
2. Selecting the Right Subject
While any type of scene can work with tilt-shift photography techniques, it’s recommended that you look for subjects that can benefit from the photography style. Identify scenes where manipulating the depth of field or perspective makes sense and adds a creative touch.
You can never go wrong with architectural elements or crowded scenes, which look great with a miniature effect.
3. Mastering the Tilt Function
The tilt function angles the lens relative to the image sensor in the camera. It changes the plane of focus, allowing you to emphasize specific parts of the subject. A crucial element in tilt-shift photography, this is a feature that you’ll have to master.
Learn to use tilt for selective focus, drawing attention to specific parts of your image. You can also experiment with different tit angles, understanding how they affect depth of field.
4. Making Use of the Shift Function
The other piece of the tilt-shift technique involves moving the lens in different directions relative to the image sensor to control perspective. You can use the shift function to help correct perspective in architecture, keeping vertical lines straight.
You can also use this function for creative composition, such as when you want to avoid some aspects at the edges of your frame.
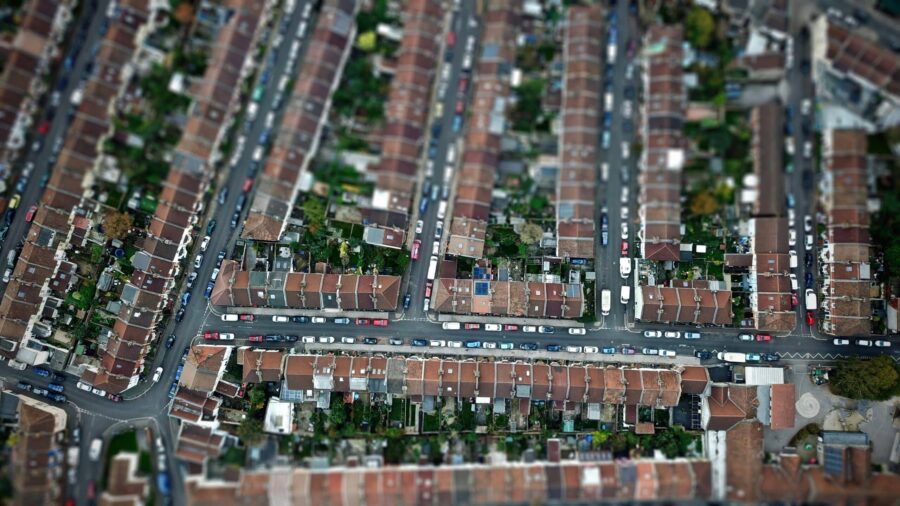

5. Adjusting Aperture Settings for Desired Effects
Your aperture settings can make or break the tilt effect you’re aiming to achieve. As such, you must find the right balance between tilt and aperture. While a wider aperture can enhance the tilt effect, you also need to look at it in relation to depth of field.
Smaller apertures, i.e., higher f-stop numbers, can increase the depth of field. This can help you capture more of the scene in focus.
6. Experimenting with Shutter Speed
Shutter speed can also affect how your tilt-shift photograph comes out. You can experiment with shutter speed to get the effect you’re looking for. Long exposures can add a dynamic element to your photograph, which is especially great when capturing landscapes and cityscapes.
A slower shutter speed can help introduce motion blur, enhancing the miniature effect of your photograph.
7. Creating a Miniature Effect
To create a miniature effect, carefully select your tilt or plane of focus. This will allow you to make large subjects look like tiny models. You can also shoot from a higher angle to enhance the miniature effect.
8. Using Tilt-Shift in Landscape Photography
Landscape photography is one of the best applications for the tilt-shift photography technique. It can add depth and scale to a landscape. Tilt, in particular, can keep both foreground and background elements in sharp focus, solving one of the biggest challenges landscape photographers face.
9. Making the Most of Tilt-Shift in Cityscape Photography
Aside from landscapes, you can also capture cityscapes with tilt-shift photography. This technique can create a stunning effect, especially in night cityscapes where the lights can create bokeh in out-of-focus areas.
Use the shift function to correct perspective and tall buildings. Conversely, use tilt to focus on urban elements.
10. Perfecting Focus with Tilt-Shift
The tilt-shift technique requires manual focusing to achieve precision. Take advantage of your camera’s live view features and focus peaking to help you focus accurately.

Tips and Tricks for Advanced Tilt-Shift Photography
Once you’ve mastered the basics of tilt-shift photography and you’re ready to explore more advanced techniques, here are some tips and tricks that can help you navigate this photography style like a pro.
Combining Tilt and Shift
The tilt-shift technique requires the simultaneous use of tilt and shift. Once you get the hang of this, you can achieve more complex and highly controlled compositions. But before that, you first have to understand how both tilt and shift movements can affect the image.
Using Tilt for Panoramic Shots
Tilt-shift lenses are great tools for capturing panoramic images, which is why they’re often used in architectural photography. You can create wide panoramas with consistent perspective by shifting the lens from left to right or right to left without moving the camera.
Focus Stacking with Tilt
To achieve front-to-back sharpness when capturing landscapes, you can use a combination of tilt for selective focus and focus stacking when post-processing.
Advanced Miniature Effect Techniques
To achieve the perfect miniature effect, don’t be afraid to experiment with different heights and angles. The most effective miniature scenes are taken from the most unexpected vantage points.
Creative Bokeh
Create unique bokeh effects in out-of-focus areas of your photograph by playing with your camera’s aperture settings. This can be especially effective in night photography or when capturing cityscapes.
Selective Coloring
When post-processing your photographs, you can selectively enhance or mute colors in focused areas, drawing more attention to certain elements and adding more layers to the tilt-shift effect.
Hyperfocal Distance Understanding
To maximize the sharpness and depth of field in your photograph, it’s important that you understand hyperfocal distance. This refers to the closest distance a lens can be focused while keeping objects acceptably sharp.
Experimenting with Different Lenses
Focal length can impact the tilt-shift effect. Wide-angle tilt-shift lenses, for example, offer a different perspective than standard or telephoto lenses. You should experiment with different tilt-shift lenses to find the effect you’re aiming for.
Using Filters
ND filters can help achieve long exposures and add motion. This can be especially helpful in daylight, enhancing the surreal effect of your tilt-shift photograph.
Tilting for Abstracts
You can also use the tilt-shift technique to create abstract images, creating unexpected compositions.

Combining Tilt-Shift With Other Techniques
You can also combine tilt-shift photography with other techniques to create more innovative and captivating photographs. Don’t be afraid to push the boundaries of your creativity. Here Are some ways you can combine tilt-shift with other photography techniques.
- Long-Exposure Photography: Use tilt-shift with long exposures to capture moving elements and add a sense of motion to the photograph.
- HDR Photography: Use tilt-shift with HDR to capture a wider range of detail and light.
- Panoramic Stitching: Shift the lens horizontally or vertically and take multiple shots to create high-res panoramic images.
- Focus Stacking: Combine tilt-shift and focus stacking to ensure sharpness.
- Black and White Photography: Use tilt-shift selective focus for black and white photography to emphasize contrast, textures, and shapes.
- Time-Lapse Photography: Use tilt-shift to create time-lapse videos and make real-world subjects look like miniature models in motion.
- Night Photography: Use tilt-shift for night photography to capture a unique cityscape perspective.
- Macro Photography: Use tilt-shift for macro photography to control the plane of focus precisely.
- Portraiture: Use tilt to focus on the subject and blur out backgrounds.
Ideas for Unique Tilt-Shift Photography Projects
If you’re looking for ideas to explore the potential of tilt-shift photography, here are some that can get you started:
- Capture a series of different cities around the world with tilt-shift
- Document landscapes or cityscapes during different seasons
- Create a time-lapse project using tilt-shift effects
- Capture the architectural details of buildings and structures
- Photograph bustling street markets with a tilt-shift lens
- Capture abandoned buildings and towns
Tilt-shift photography is a fascinating technique that will take you through a journey of creative exploration. In this guide, we covered the top methods that will help you master the unique style, from the basics of camera positioning to understanding the tilt and shift functions.
As you embark on your tilt-shift photography journey, remember that each scene you capture is an opportunity to see the world from a different perspective, to tell a story, and to explore your creative expression.